Source: David L. Chandler, MIT News
March 22, 2016
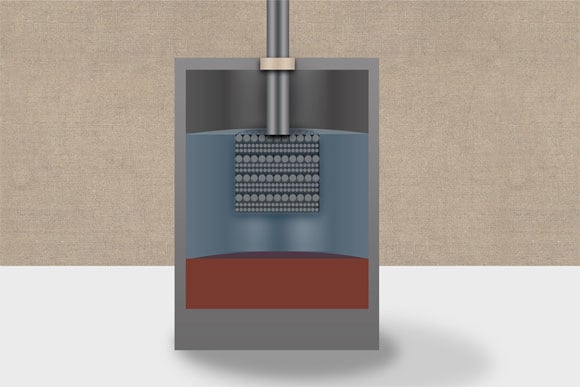
An artist’s rendering of a calcium liquid battery.
In a newly published study, MIT researchers show that calcium can form the basis for both the negative electrode layer and the molten salt that forms the middle layer of the three-layer battery.
Liquid metal batteries, invented by MIT professor Donald Sadoway and his students a decade ago, are a promising candidate for making renewable energy more practical. The batteries, which can store large amounts of energy and thus even out the ups and downs of power production and power use, are in the process of being commercialized by a Cambridge-based startup company, Ambri.
Now, Sadoway and his team have found yet another set of chemical constituents that could make the technology even more practical and affordable, and open up a whole family of potential variations that could make use of local resources.
The latest findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications, in a paper by Sadoway, who is the John F. Elliott Professor of Materials Chemistry, and postdoc Takanari Ouchi, along with Hojong Kim (now a professor at Penn State University) and PhD student Brian Spatocco at MIT. They show that calcium, an abundant and inexpensive element, can form the basis for both the negative electrode layer and the molten salt that forms the middle layer of the three-layer battery.
That was a highly unexpected finding, Sadoway says. Calcium has some properties that made it seem like an especially unlikely candidate to work in this kind of battery. For one thing, calcium easily dissolves in salt, and yet a crucial feature of the liquid battery is that each of its three constituents forms a separate layer, based on the materials’ different densities, much as different liqueurs separate in some novelty cocktails. It’s essential that these layers not mix at their boundaries and maintain their distinct identities.
It was the seeming impossibility of making calcium work in a liquid battery that attracted Ouchi to the problem, he says. “It was the most difficult chemistry” to make work but had potential benefits due to calcium’s low cost as well as its inherent high voltage as a negative electrode. “For me, I’m happiest with whatever is most difficult,” he says — which, Sadoway points out, is a very typical attitude at MIT.
Another problem with calcium is its high melting point, which would have forced the liquid battery to operate at almost 900 degrees Celsius, “which is ridiculous,” Sadoway says. But both of these problems were solvable.
First, the researchers tackled the temperature problem by alloying the calcium with another inexpensive metal, magnesium, which has a much lower melting point. The resulting mix provides a lower operating temperature — about 300 degrees less than that of pure calcium — while still keeping the high-voltage advantage of the calcium.
The other key innovation was in the formulation of the salt used in the battery’s middle layer, called the electrolyte, that charge carriers, or ions, must cross as the battery is used. The migration of those ions is accompanied by an electric current flowing through wires that are connected to the upper and lower molten metal layers, the battery’s electrodes.
The new salt formulation consists of a mix of lithium chloride and calcium chloride, and it turns out that the calcium-magnesium alloy does not dissolve well in this kind of salt, solving the other challenge to the use of calcium.
But solving that problem also led to a big surprise: Normally there is a single “itinerant ion” that passes through the electrolyte in a rechargeable battery, for example, lithium in lithium-ion batteries or sodium in sodium-sulfur. But in this case, the researchers found that multiple ions in the molten-salt electrolyte contribute to the flow, boosting the battery’s overall energy output. That was a totally serendipitous finding that could open up new avenues in battery design, Sadoway says.
And there’s another potential big bonus in this new battery chemistry, Sadoway says. “There’s an irony here. If you’re trying to find high-purity ore bodies, magnesium and calcium are often found together,” he says. It takes great effort and energy to purify one or the other, removing the calcium “contaminant” from the magnesium or vice versa. But since the material that will be needed for the electrode in these batteries is a mixture of the two, it may be possible to save on the initial materials costs by using “lower” grades of the two metals that already contain some of the other.
“There’s a whole level of supply-chain optimization that people haven’t thought about,” he says.
Sadoway and Ouchi stress that these particular chemical combinations are just the tip of the iceberg, which could represent a starting point for new approaches to devising battery formulations. And since all these liquid batteries, including the original liquid battery materials from his lab and those under development at Ambri, would use similar containers, insulating systems, and electronic control systems, the actual internal chemistry of the batteries could continue to evolve over time. They could also adapt to fit local conditions and materials availability while still using mostly the same components.
“The lesson here is to explore different chemistries and be ready for changing market conditions,” Sadoway says. What they have developed “is not a battery; it’s a whole battery field. As time passes, people can explore more parts of the periodic table” to find ever-better formulations, he says.
“This paper brings together innovative engineering advances in cell design and component materials within a strategic framework of ‘cost-based discovery’ that is amenable to the massive scale-up required of grid-scale applications,” says Richard Alkire, a professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of Illinois, who was not involved in this research.
Because this work builds on a base of well-developed electrochemical systems used for aluminum production, Alkire says, “the path forward to grid-scale applications can therefore take advantage of a large body of existing engineering experience in areas of sustainability, environmental, life cycle, materials, manufacturing cost, and scale-up.”
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Energy (ARPA-E) and by the French energy company Total S.A.
Publication: Takanari Ouchi, et al., “Calcium-based multi-element chemistry for grid-scale electrochemical energy storage,” Nature Communications 7, Article number: 10999; doi:10.1038/ncomms10999